In the United States, there are 130,930 recorded number of K-12 schools in the United States of America (U.S.A), according to the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES). This means on average there are 2,618 schools per state, with some states like California and Alaska being above and below the curve, respectively. While this may appear to be large, the trend actually points to a decrease in total schools since 1930, when there were over double the current number of schools in America. However, the average number of students per school has accordingly doubled as well.
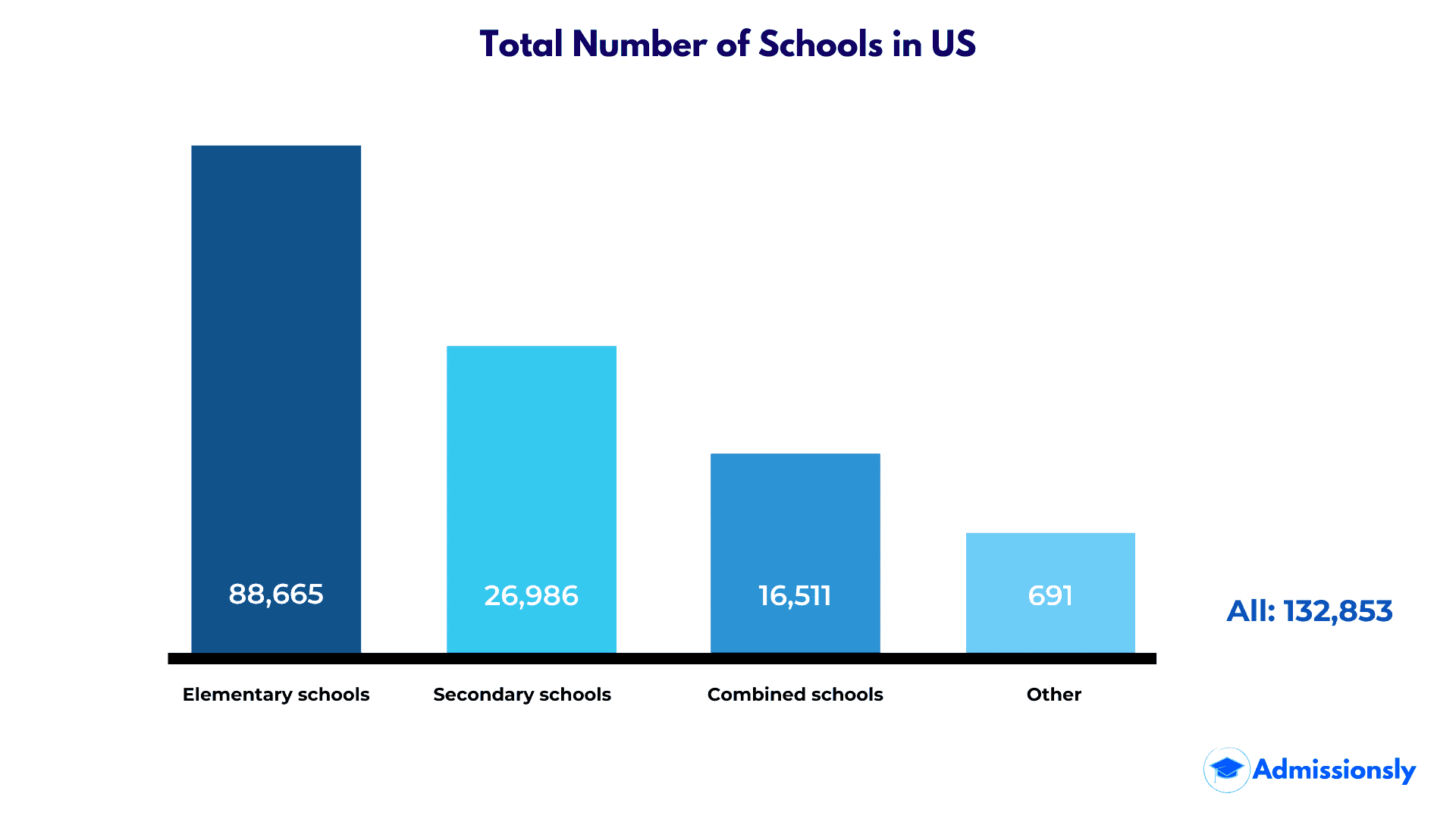
Despite there being 130,930 schools, not all schools fit under the same umbrella. The number of high schools in the US are 26,727, while the total number of elementary schools is about four times that amount at 87,498.
Does further data analysis ask questions like: how many students who graduate from high school are likely to acquire a high-paying job? Which students in each geographic region of the U.S. tend to do better on standardized tests? Some argue ACT scores do not matter in the long run, while others may strongly disagree.
Are private schools worth the extra money, or can you receive a satisfactory education in today’s modern public school system? The school facts and data say no, you cannot earn a satisfactory education in the public school system if you plan to enroll in college, however, enrollment has still increased across the board for public schools, both in elementary and secondary categories.
 Learn more statistics about school in 2020 below.
Learn more statistics about school in 2020 below.
10 Key General Public School Statistics
- More than 50.8 million students K-12 are expected to attend public schools by 2020.
- The average public school U.S. enrollment is 528 students per school.
- According to a high school statistics report on crime and safety, students who did not plan to complete 4 years of college consistently reported higher rates of heroin use and use of OxyContin and Vicodin, during the past 12 months than students who had plans to complete 4 years of college.
- The number of all public elementary schools (schools beginning with grade 6 or below and ending with grade 8 or below) increased 4 percent between 1970–71 and 2006–17 (64,000 and 66,800, respectively).
- In the 2016–17 school year, the adjusted cohort graduation rate (ACGR) for public high school students was 85 percent, the highest it has been since the rate was first measured in 2010–11.
- Of the 87,498 elementary schools in the US, 67,408 are public schools.
- In the 2015–16 school year, a higher percentage of traditional public schools compared to public charter schools had at least one school nurse (84 percent compared to 52 percent).
- 46 states prove that graduating from public high school doesn’t immediately qualify you for local universities.
How Many Public Schools in the US?
Public education facts provided by educationdata.org report that there are 97,568 public schools in the U.S. Of these public schools, approximately 67, 408 are elementary schools and 30,160 are public secondary schools. This number is a substantial jump from the first record of public schools in 1929, which was noted at 248,000 (nces.ed.gov). While enrollment statistics are positive for growth in public schools, the leading minority matriculate close to half the number of white students. The total amount of spending on public schools is expected to reach $680 billion.
Other key statistics on the number of public schools in the U.S.:
- Between 2000 and 2016, public schooling statistics show that enrollment increased for 32 states. To date, 2019 will be the highest enrollment count for public schools, ever. (nces.ed.gov)
- The highest demographic for public school students is White students at 23.7 million. The highest leading minority enrollment is Hispanic students at 13.9 million. The lowest percentage demographic is Pacific Islander students at 0.2 million. (educationdata.org)
- There are about 50.8 million public schools in us. Since an estimated $680 billion will be spent to fund them, it is estimated that each student will cost about $13,440. (edweek.org)
How Many Private Schools in the US?
Educationdata.org reports that the total number of private schools in the U.S. is 32,461. Of these private schools, the most dominant religious sect is Catholic, with 38.8% of the total sample. The last ranked private school by popularity is Islamic, with 0.8% of the sample, according to capenet.org. Private school statistics show, however, that this gap is decreasing over the years. From 1991 to 1992, Catholicism sampled for 53% of private schools, while Islamic accounted for 0.1%, meaning Catholicism went down 14.2% and Islamic went up 0.7%.
Private schools offer different benefits compared to their public school counterparts. While public schools are mostly funded through the government, private schools do not receive the same funding. US School statistics show, however, that private schools tend to score higher on the ACT.
Other key statistics on private schools in the US:
- The U.S. Census Bureau reports that of the 10.9 million families with children in grades K-12 that also earn over $75,000, only 11% of them have children in private schools. This means, in the majority of cases, families in the highest income bracket send their kids to public schools. (US Census Bureau)
- Private schools rely heavily on student enrollment as a main source of income, to compensate for lack of government funding. Industry revenue is expected to grow 1.5% alone in 2019, increasing at an annualized rate of 3.8% to $87.5 billion over the five years to 2019. (Ibisworld.com)
- Private schools tend to score higher on composite ACT scores. Private schools scored on average a mean composite score of 23.8, whereas public school graduates scored on average a mean composite score of 20.7. Overall, the scores remained consistent across the different sections of the ACT. (Cape Outlook)
How Many High Schools are in the US?
The total number of high schools in the U.S. is expected to reach about 26,727, according to Educationdata.org. This means that high schools will comprise about 31% of all schools K-12. Between public and private high schools, there are 23,882 public schools and 2,845 private schools, respectively. Combined, private and public schools will host a total of 15.1 million high school students, which means there will be about 565 students per school. In 2020, approximately 3.3 million students will graduate from public high school and 0.4 million from private high schools.
Other key facts about high schools in the US:
- Of the total high schools in the USA, there are 15.3 million students. This number has been steadily increasing as there were 13.5 million students in 2000 and 13.2 million in 1980.
- 70 percent of graduates who went on to postsecondary education either had earned a credential in an occupational field by 2016 or found a job in a related field. This means that about 1/5 of high school graduates will drop out of college. More than 1/3 will still be in college after 6 years.
- The compensation for teachers varies by geographic location. Teachers in New York, for example, make about $84,000, while teachers in Mississippi make about $45,000. In other words, teachers in New York get back close to 100% more than teachers in Mississippi.
- According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics, high school teacher median pay was $61,660 in 2019. There were about 1,072,500 teachers in high school, which means there were about 45 teachers per high school.
- The growth of junior high schools in us has seen a positive trend since 1980. From 1980-1981, there were 1,743 combined elementary and secondary schools. The most recent recordings show that combined schools are now at 6,783.
How Many K-12 Schools in the US?
There are approximately 130,930 K-12 schools in the U.S., according to the most recent report from the National Center for Education Statistics (NCES). This number is substantially higher than the number of K-12 schools in 1980, which was 106,746. States have been the primary funders for their K-12 schools, while the federal share of K-12 spending has risen from 5.7 percent to 8.3 percent over the past twenty years. This number is expected to increase steadily over the next few years, according to the NCES.
- There will be approximately 3.7 million teachers in the fall of 2019, meaning on average there will be about 27 teachers per school and 15 students per teacher. According to the bureau of labor statistics, teaching jobs are projected to grow at about 3% each year. (educationdata.org)
- 56.6 million students enrolled in k-12 in 2019. 50.8 million will be in public school, and 5.8 million will be in private school. The contrast in student enrollment is mostly attributed to the cost. Whereas public schools are paid for mostly by the government and therefore taxpayers, private schools cost an additional fee, usually ranging from $10,000 to $15,000. (nces.ed.gov)
- An estimated $13,440 will be spent on each student in PK-12 education 2020. This is about the same cost required to enroll in a private school, however, enrollment with public schools does not require the same payment upfront because most of it is paid through the government. (educationdata.org)
Elementary and Secondary Schools Statistics
Elementary schools have experienced the greatest increase in enrollment when compared to secondary schools. In total, elementary schools have about 56.6 million students. Elementary school statistics display that the growth of these schools is trending even further upwards, with estimates as high as 86 million by 2027. This number is, however, lower than the trend has been in recent decades, according to educationdata.org. The most recent estimates of secondary school enrollment as well as elementary middle high schools postulate that by 2018, the total number of students was 15.3 million. The rise in elementary middle high schools is to consolidate schools where enrollment may be failing.
- The number of secondary schools has decreased steadily over the years. In 2000, for instance, the number of high schools in the US was 27,575. In 2018, however, that number has decreased to 26,727 (educationdata.org)
- In total, 77% of secondary school teachers are female and 23% are male, meaning males make up about a quarter of all high school teachers. About half of the teachers had a postbaccalaureate whereas 90% had some form of certification. (educationdata.org)
- Elementary and secondary enrollment increased by 6% between 1996 and 2010. These numbers are projected to increase by 7% by 2021, according to NCES. This means the enrollment in elementary and secondary institutions is projected to increase 13% by 2021. (nces.ed.gov)
- In 2014, whites accounted for 52% of enrollment in elementary and secondary schools. However, in 2016, they accounted for 48%. The next leading minority for enrollment is Hispanics, at 26%.
American Charter VS Traditional Publics Schools Statistics
- A charter school is a school that typically relies on public funding but is also governed by another group under legislative contract. There were more than 7,010 charter schools in 2017, the last recorded date for charter schools in the U.S. Currently, there are also 99,154 traditional public schools. (educationdata.org)
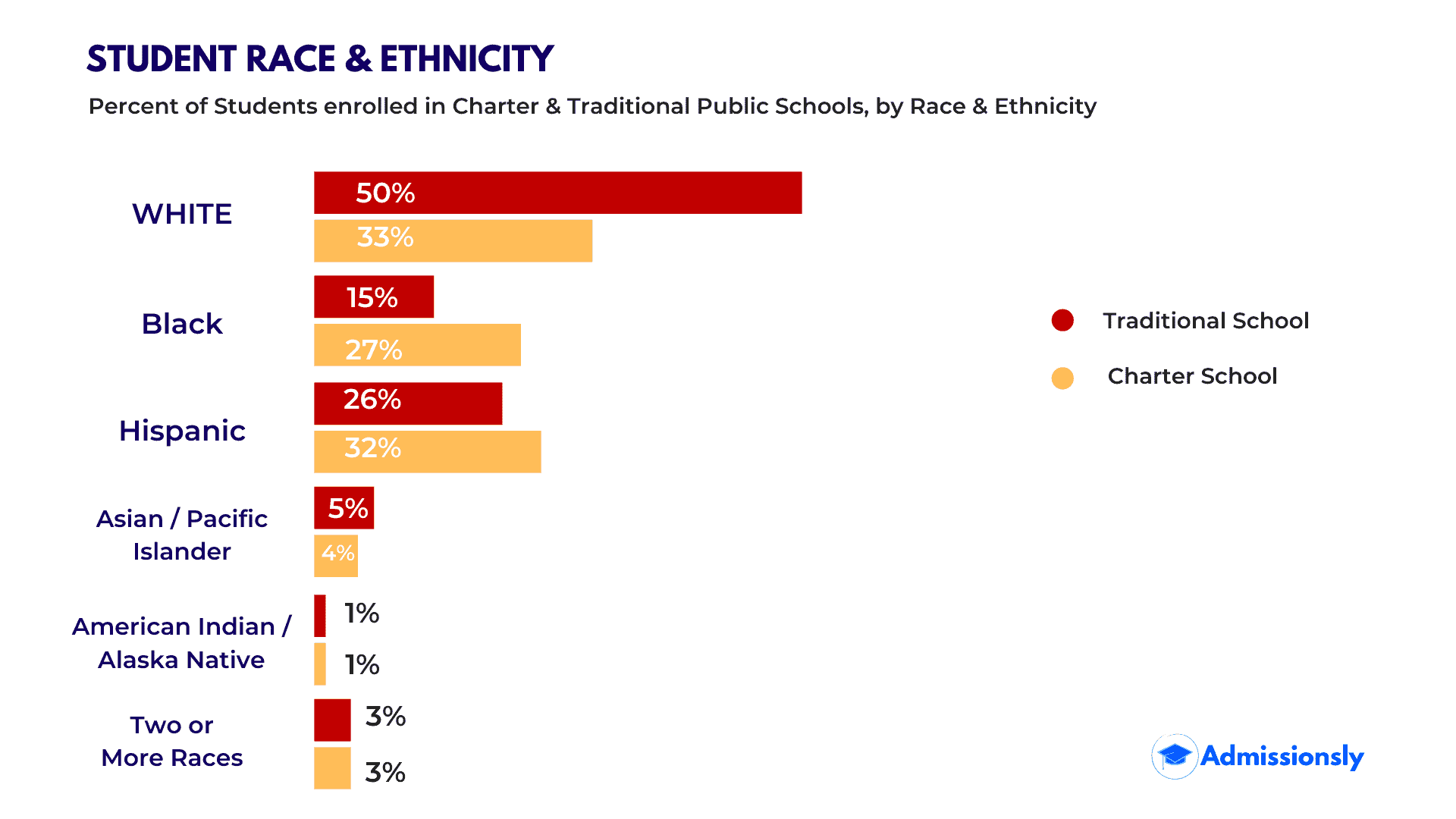
- There is a difference in ethnic enrollment for charter schools. 57.4% of charter schools had more than 50% of white enrollment, whereas 8.8% of charter schools had more than 50% black enrollment, strongly construing that the enrollment of whites is much higher than that of blacks, or Hispanics. Hispanics we are in the middle, with 50% of enrollment in 16.3% of charter schools. (nces.ed.gov)
 Charter school enrollment has grown more than 7% from 2009-10 to 2015-16, according to NCES. Charter schools with over 300 students have increased enrollment, however, those with less have decreased their enrollment. (nces.ed.gov)
Charter school enrollment has grown more than 7% from 2009-10 to 2015-16, according to NCES. Charter schools with over 300 students have increased enrollment, however, those with less have decreased their enrollment. (nces.ed.gov)
- In 1991, the first law allowing the establishment of public charter schools was made to pass in Minnesota. In 2016, that same law would be passed in 43 states, meaning charter schools are most likely not going anywhere. (nces.ed.gov)
- In 2016-2017, about two-thirds of charter schools were independently created and maintained by groups of teachers, community groups, universities, foundations, businesses or faith-based groups. One-third, however, were created by management organizations that operate multiple schools. The latter is a combination of non-profit and for-profit. (nces.ed.gov)
Quick Look About Specializing Public Schools
Special Education Schools: School geared towards people with special needs including conditions like down syndrome, cerebral palsy, or even behavioral issues.
- In 2017, 13.7% of all students were special education students. This means that roughly 1 in 10 students are students with special needs. (nces.ed.gov)
- States with the highest amount of special education students include New York and Massachusetts at about 17%, whereas states such as Texas and Hawaii have lower rates at about 10%. (thejournal.com)
Magnet Schools: Schools that are public but also offer specialized courses. Magnet schools typically receive specialized funding from the government to maintain their specialized courses.
- The number of magnet schools in the United States reached 3,421 in 2018. This is a slight increase from the previous year, which had about 3,164 magnet schools. (statista.com)
- Fall enrollment for magnet schools in 2015 reached 2,609,104, equating to roughly 4% of total students, which is 50,009,771 students total. (nces.ed.gov)
Vocational Schools: Schools that provide practical skills training as opposed to academic study, or a traditional school route. This school is a useful path for people who are looking to enter the industry for the first time, reenter the workforce, or pursue a new field.
- Common programs for vocational schools include welding, cosmetology, plumbing, carpentry, locksmithing, electrical installation and maintenance, motorcycle and automotive repair, floral design, medical transcription, and hotel and restaurant management. These professions require technical knowledge, but not as much of the rigorous academic pressure a biology major might be dealt with. (www.study.com)
Alternative Schools: Schools that offer specific accommodations for the behavioral or medical needs of students that can not be relied on in a traditional education setting.
- Common students may have experiences with substance abuse, personality disorders, depression, violence, and other personal issues that can inhibit functioning in a traditional environment. (nces.ed.gov)
- Roughly 32% of students enroll after facing some degree of educational failure in the traditional school system. (nces.ed.gov)
What is the Average School Size?
The average school size in the U.S. is approximately 526 students. The average school size varies further when considering the location. City schools, for example, average about 591 students, while suburban schools average about 656 students. Town level students see a decrease at an average of 444 students and rural even further at an average of 358 students.
Other key facts about school sizes in the U.S.:
- There are 13,598 school districts in the U.S. If there are 130,930 schools in the U.S., that means there are on average about 10 schools per district. (edweek.org)
- The current average quantity of students in school is up 8 students average from 2011. The number, however, is an increase for elementary schools, and a decrease for secondary schools. (edweek.org)
Conclusion
The number of schools is changing, and while some areas like elementary schools are growing larger, other systems like secondary schools are closing. The trade-off, in these statistics, however, is the secondary schools are gaining more students, while the elementary schools are losing students.
Some crucial factors like racial diversity are still uneven, however, they have been improving over the years. Whites, for example, accounted for over 50% of students in 2000, but now they account for about 38%. The United States has about 77 million students in total, which means there are a lot of minorities out there. Every state is different, however, and some need more assistance than others. Overall, enrollment rates will continue to rise at a steady rate.
Special schools, vocational schools, alternative schools, and magnet schools are also on the rise as more and more legislators, teachers, parents, and organizations work together to create more flexible educational opportunities for children with special needs.
Above all else, it’s important to keep tracking our educational standards and to create equal and fair opportunities for everyone to succeed.

